



Many people assume that because herbs are natural, they are safe for consumption. This is not always the case, because many plants are poisonous or have some toxic component to them. When mixed with chemical drugs, there may be undesirable side effects. The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) currently provides a detailed list of articles (approximately 86 pages) about specific herbs and their possible contraindications with drugs.
In 2012, the International Journal of Clinical Practice published an Evaluation of Documented Drug Interactions and Contraindications Associated with Herbs and Dietary Supplements authored jointly by H.H. Tsai, H.W. Lin and H.Y. Tsai of China Medical University in Taiwan, and A. Simon Pickard and G.B. Mahady of the University of Illinois at Chicago. While 85 primary literatures, six books and two websites were reviewed for a total of 1,491 unique pairs of herb-drug interactions, 213 herbal entities and 509 medications were involved.
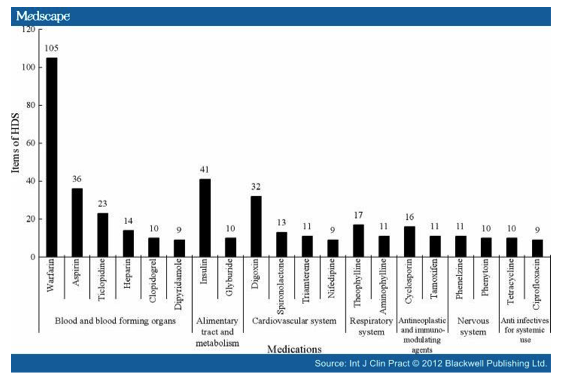
The top five herbs/botanical products, which were documented to have the most interactions with individual medications, were St John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum), ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba), kava (Piper methysticum), digitalis (Digitalis purpurea) and willow (Salix alba). On the other hand, warfarin, insulin, aspirin, digoxin and ticlopidine had the biggest number of reported interactions with herbs.
Overall, medications that affect the central nervous system or cardiovascular system had more documented interactions with herbs. Of the 152 identified herbal contraindications, the most frequent involved gastrointestinal (16.4 percent), neurological (14.5 percent) and renal/genitourinary diseases (12.5 percent). Flaxseed, Echinacea and yohimbe had the largest number of contraindications. The chart below shows the medications with the highest incidences side effects when used in conjunction with herbal dietary supplements (HDS).
The report acknowledges that there are many potential herb-drug interactions that may exist but are without documented outcomes. Since only reports, books or articles published in English were included in this review, it is likely that the interactions in this review are under-reported, since traditional herbal medicine is practiced widely in Asia.
Rule of thumb: Contact your health care provider if you discover that a possible drug interaction may occur between your medications and herbal products that you use. Do not stop taking your medication unless directed to do so by your physician. The interaction may be insignificant, in which case no change is necessary. Your doctor can tell you if the medication and/or the herbal supplement needs to be discontinued.